Light G Bands That Appear Along Chromosomes Contain ...
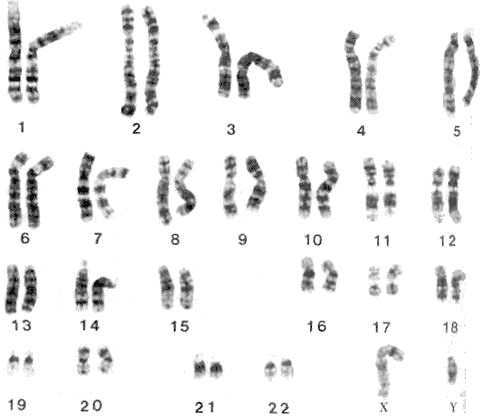
G binds to C. A Ideograms of chromosome 1 at the 550-band and the 850-band level.

G Band Ideograms Of Human Chromosome 11 At From Left To Right 350 Download Scientific Diagram
3 R-banding - gives the reverse of G-banding dark G-bands appear light light G-bands appear dark.
. Figure 4 shows the proportion of genes per group by chromatin G-band intensity with light to dark banding scaled numerically by color from 1 to 5. G bands Are darkly stained regions of compacted chromosomes heterochromatin that have been stained with Giemsa 16. An ideogram is an idealized representation of the banding pattern.
As shown the proportion of protein-coding genes. A unique banding pattern is used to identify each chromosome. On using this stain dark and light bands appear.
The staining of chromosome is known as banding technique because stains give rise to pattern of bands along the length of chromosome. G-banding is the most frequent used technique for chromosome staining in cytogenetics. Light G bands that appear along chromosomes contain.
Part B Light G bands that appear along chromosomes contain. Because G-dark bands contain fewer genes and are less GC-rich than G-light bands Craig and Bickmore 1993 it is not surprising to observe a significant correlation between chromosome gene number GC content and centromere localization Figure 3c. -Condensation of the DNA in these regions is variable throughout the cell cycle.
Chromosomal Banding A chromosome banding pattern is comprised of alternating light and dark stripes or bands that appear along its length after being stained with a dye. However none of these variables alone adds any significant explanatory power to the above. It is still not clear why chromosomes show bands when they are stained with quinacrine or Giemsa.
Giemsa also creates a reproducible pattern of bands on each chromosome. G-Q and R-bands these bands are distributed along the length of the whole chromosome. Euchromatin Is the relatively less condensed region of chromosomes 17.
Giemsa staining is an excellent nonfluorescent staining techniques. This representation is used for comparison to height profiles along chromosomes. However none of these variables alone adds any significant explanatory power to the above model p 0025.
Heterochromatin Is the relatively more condensed region of chromosomes 18. The band pattern is different for different chromosome. A chromosome banding pattern is comprised of alternating light and dark stripes or bands that appear along its length after being stained with a dye.
The tightly packed DNA is heterochromatin AT rich takes more dye and stains dark. A unique banding pattern is used to identify each chromosome and to diagnose chromosomal aberrations including chromosome breakage loss duplication or inverted segments. C-bands centromeric bands and NORs nucleolus organizer regions.
This is an international system. Part B Light G bands that appear along chromosomes contain. An alien species was discovered that has DNA comprised of 6 different bases.
However an asymmetric distribution pattern of ASD obesity and protein-coding genes over the range of G-band intensity levels was observed across the genome. 2 By examining chromosomes at. Using this abnormalities of chromosomes can be determined.
They are used to stain a restriction number of specific bands or structures. -Chromatin is tightly condensed. Dark and light bands represent G and R bands respectively.
Approximately 16 of this alien genome is comprised of nucleotides containing C and 22 is comprised of nucleotides containing Y. Chromosome 1 contains a large block of heterochromatin close to the centromere grey. 1 Bands along each arm are numbered starting at the centromere.
A unique banding pattern is. A binds to T. Because G-dark bands contain fewer genes and are less GC-rich than G-light bands Craig and Bickmore 1993 it is not surprising to observe a significant correlation between chromosome gene number GC content and centromere localization Figure Figure3c.
They appear as light color bands upon staining in G banding whereas heterochromatin appears darkly stained. G banding is giemsa banding which means staining with giemsa stain in karyotyping the chromosomes. And X binds to Y.
A chromosome banding pattern is comprised of alternating light and dark stripes or bands that appear along its length after being stained with a dye. R-banding is a useful complement to G-banding because some small light G band can be more easily detected when they are. Telomere is located at the end of chromosome that contains repetitive nucleotide sequences and centromere is located at the center of chromosome which links the sister chromatids thus they are not applicable.
B The banding pattern is characteristic for each chromosome pair. -Most expressed genes or genes that are actively transcribed are located here. -These regions contain fewer expressed genes or fewer genes that are actively transcribed.
The bands appear only when the chromosomes are exposed to ultraviolet UV light. C-banding methods do not permit identification of every chromosome in the somatic cell complement but can be used to identify specific. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect.
Solved Part A Dark G Bands That Appear Along Chromosomes Chegg Com

G Banding An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Chromosome Identification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

G Banding An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Chromosome Banding And Mechanism Of Chromosome Aberrations Intechopen

Komentar
Posting Komentar